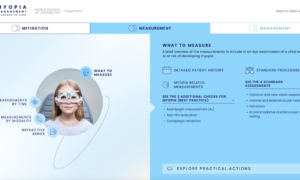
Due to the drastic increase in both the prevalence and severity of myopia in China, on August 30, 2018, eight national departments jointly issued the “Comprehensive Prevention and Control of Myopia in Children and Adolescents Implementation Plan” with the goal of controlling the prevalence of myopia in the population of 6-year-olds or younger at about 3 percent by 2030. The effort has expanded to involve another seven governmental ministries.
Here are some highlights from the Implementation Plan:
Parents Should:
- Adapt basic scientific knowledge of the development of vision and the eye to help children develop good visual habits. Birth to 6 years old is a critical period for children’s visual development.
- Pay special attention to their children’s early visual development and seek early intervention when myopia is detected. Birth to 6 years is a critical period.
- Encourage their children to increase outdoor activities.
- Limit their children’s use of electronic products and minimize their own use of electronic products when accompanying their children.
- Enforce visual relaxation after using electronic products for 30 to 40 minutes.
- Monitor their children’s visual behavior and provide constant feedback to correct unhealthy behavior, guiding children to not read or use electronic products when walking, eating, lying in bed, in low light, or in direct sunlight.
- Supervise and correct children’s incorrect reading and writing posture at any time.
- Ensure sufficient sleep and nutrition for their children.
- Take their children for an early vision examination and follow the professional’s advice to carry out scientific intervention and avoid non-scientific based methods to control myopia.
Schools Should:
- Manage homework by grade and subject groups. Written homework is not assigned to the first and second grades of elementary school. Time required for written homework in the third to sixth grades should not exceed 60 minutes, and that of junior high school should not exceed 90 minutes.
- Control exams with no more than one per semester for the first and second grades and no more than twice per semester for other grades.
- Improve the visual environment to meet visual hygiene requirements with standard adjustable desks and chairs and lighting conducive to healthy eyesight.
- Ensure more than one hour of outdoor physical activity a day.
- Limit use of electronic products to no more than 30 percent of total teaching time.
- Regularly carry out vision screening. Primary schools should receive electronic files of children’s and adolescents’ vision health transferred from medical and health institutions to ensure one file per person and transfer them in real time as the student’s status changes.
- Under the guidance of the health department, strictly implement the student health check-up system and twice-a-semester vision monitoring system, remind and educate students with abnormal vision, and promptly inform parents to take students to get a comprehensive visual examination. Provide statistical analysis and data summary of new incidences of poor eyesight among students, and cooperate with medical and health institutions to carry out vision screening.
- Strengthen vision health management. Establish a vision health management team that integrates school administrators, teachers, school doctors, parent representatives, student vision protection committees, and volunteers to clarify and refine responsibilities. Incorporate myopia prevention and control knowledge into classroom teaching, campus culture, and students’ daily behavior norms. Improve facilities and equipment of school clinics to allow basic vision screening and urgent troubleshooting.
Medical and Health Institutions Should:
- Create a children’s vision database. Strictly implement the requirements of the national basic public health service for the eye care and vision examination of children from birth to 6 years, and achieve early monitoring, early detection, early warning, and early intervention. The target coverage rate for an annual vision exam in children from birth to 6 years is 90 percent starting in 2019.
- Standardize diagnosis and treatment. General hospitals at the county level and above should generally provide ophthalmic medical services, earnestly implement the “Myopia Prevention and Control Guidelines” and other diagnostic and treatment standards, and continuously improve eye health service capabilities. For children and adolescents with high myopia or pathological myopia, the risks of complications should be fully informed. Give full play to the role of Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of myopia, formulate and implement a comprehensive treatment plan that integrates Chinese and Western medicine, and promote the application of Chinese medicine in the field.
- Strengthen health education starting with disease awareness education at the public health level. In response to people’s lack of knowledge about myopia prevention and treatment and insufficient awareness of the seriousness of myopia hazards to health, give full play to the guiding role of experts in health management, public health, ophthalmology, optics, disease prevention and control, and Chinese medicine.
Government Agencies Are Addressing Myopia
Multiple government agencies have also been enlisted to participate in a nationwide initiative to address the myopia epidemic in China. Here are some examples:
The Ministry of Education is improving school sports and health education projects and encouraging colleges and universities, especially medical colleges, to set up majors in ophthalmology, health management, and health education. It is also training specialists in myopia prevention, vision health management, and health education, and researching vision health management for children and adolescents.
The Ministry of Education has also instructed schools to begin paying attention to the visual habits of students during school hours, including the implementation of eye exercises, outdoor activities, specifications of classroom desks and chairs, and improvements in lighting.
The National Health Commission is involved by training vision health professionals and setting up prevention and control sites. It is strengthening the training of primary-level ophthalmologists, vision care practitioners, and pediatric practitioners to improve vision screening, diagnosis and treatment of common eye diseases, and emergency treatment. It is also ensuring that every county (city, district) has qualified optometrists to provide standardized services. In addition, the National Health Commission is enhancing the national children and adolescents’ vision health and related risk factors monitoring network, data collection, and information construction. Standards have been issued to strictly regulate the fonts and paper of printed matter for children and adolescents.
The General Administration of Sports will increase venues and facilities suitable for outdoor activities and physical exercises for children and young people, and continue to promote the opening of various public sports facilities to children and young people.
The General Administration of Market Supervision and Administration is strictly supervising optometry, opticianry, and ophthalmic products, and increasing inspections on the production, circulation, and sales of spectacle lenses to prevent substandard spectacle lenses from entering the market. It is also investigating advertising to deal with false and illegal myopia prevention and control product advertisements in accordance with the law.